The blockchain is booming with interesting new protocols and projects, and today, we’d like to focus on one in particular: Razor Network. Razor Network is a Proof-of-Stake consensus-based blockchain network with, at its core, a set of smart contracts that can run on any Ethereum-compatible blockchain. Razor relies on the underlying blockchain to provide properties such as censorship resistance, network partition security, etc.
Razor Network aims to provide a decentralized method for verifying and providing data to a blockchain. Because entire economies are being built on blockchains that rely heavily on external data, it is critical that the data is provided and aggregated in a decentralized manner to avoid many attacks. For example, Razor Network is resistant to bribing attacks because it utilizes a high degree of redundancy and offers high economic security for all applications regardless of the fees paid to the oracle. Additionally, the Razor network can dispute Oracle's results, making it resistant to various game theoretical flaws.
The Razor network employs a proof-of-stake consensus algorithm and a native utility token known as $RAZOR. To participate as a stakeholder in the network, $RAZOR must be locked. Stakers are compensated with fees and block rewards for their participation in the network. The staker's influence in the network is determined by the number of tokens they have staked.
An Overview of Razor Network
It’s important to note that Razor Network is built up out of four different parts known as the Oracle, Collection Manager, Client Application, and User. The Oracle is made up of stakeholders who process queries in the job queue and return the results to the client application as needed. To become a staker in the Oracle platform, a staker must lock their $RAZOR. Before submitting it to the Oracle contract, the stakeholders query the data source as specified in the job specifications and perform the necessary data processing operations on it. The finalized value is then reported to the requested contract after aggregation. Because the validation cycle is automated, the validation client can be run by stakeholders with almost no manual intervention. But it’s important to remember that some jobs may be manual and require manual reporting by stakeholders. Also, if a result is disputed, the dispute rounds will be manual.
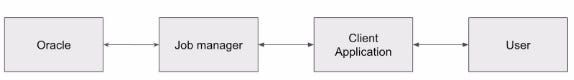
The Collection Manager receives queries from client applications and prioritizes them based on the fees paid. The oracle will prioritize queries with higher fees for processing. The collection manager can handle both single requests and data feed requests.
Then there’s the Client Application, which is an application that uses the blockchain Oracle. It’s very straightforward, because Razor is a permissionless general-purpose oracle platform any smart contract application or user can pay the fees to utilize its services. Finally, the User might be the most important part of the ecosystem. While oftentimes the user might not even know that the Razor Network is being used in the background to fetch data, their use of the client applications is what makes Razor Network.
Razor Network’s Native Asset
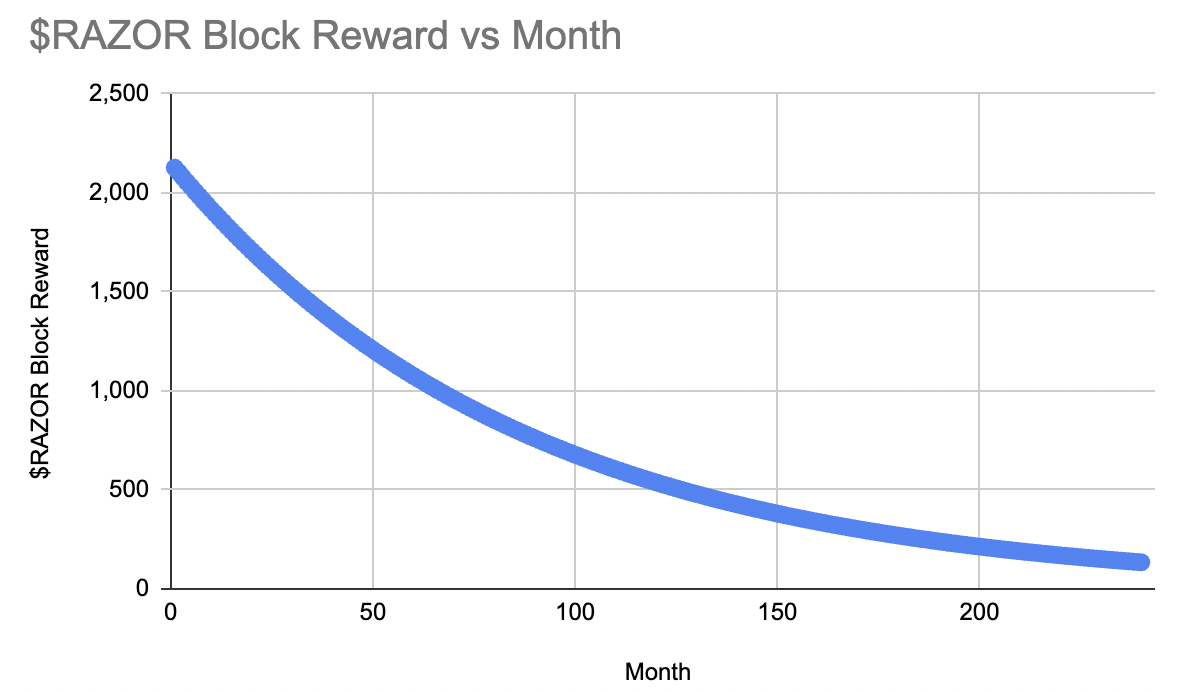
Razor Network’s utility token is called $RAZOR, and is an Ethereum Mainnet token standard known as ERC-20. Within the ecosystem, $RAZOR is required for security such as staking, governance decisions, transactions etc. According to Coinmarketcap, the total initial supply is 1,000,000,000 $RAZOR. At genesis, the block rewards were set in such a way to encourage staker participation, over time the block rewards will decrease.
Staking $RAZOR
To learn more about staking $RAZOR, have a look at our step-by-step video below.
Final Thoughts
Razor Network is a blockchain-agnostic, decentralized oracle platform designed to meet the wide range of Decentralized Finance requirements. Stakin believes that Razor Network is developing the next-generation Oracle system with a focus on maximum game-theoretical security and complete permissionless decentralization, and is looking forward to contributing to the Mainnet and its ever expanding ecosystem.
DISCLAIMER: This is not financial advice. Staking, delegation, and cryptocurrencies involve a high degree of risk, and there is always the possibility of loss, including the failure of all staked digital assets. Additionally, delegators are at risk of slashing in case of security or liveness faults on some protocols. We advise you to do your due diligence before choosing a validator.



