Hi Readers👩💻,
We recently introduced the staking guide for Akash Network. However, for those of you who aren’t familiar with this network yet, today, we’re breaking down everything you should know about it. So, let’s dive right in.
Akash is a secure, transparent, and decentralized cloud computing marketplace that connects those who need computing resources with those that have the computing capacity to lease.
Akash, also called Akash DeCloud, consists of two main components: the network and the platform. The Akash Network is an on-chain decentralized marketplace for leasing computing resources. While the Akash Platform is an off-chain deployment platform used for hosting and managing workloads and is a set of cloud management services that leverage Kubernetes to run workloads.
The Akash Network is a Tendermint based blockchain application built with Cosmos SDK.
The Akash Network Marketplace
The Akash Network marketplace acts as a supercloud platform that provides a unified layer above all providers on their marketplace (network) to ensure clients have a single cloud platform, regardless of which particular provider they may be using. People use the Akash Network rather than traditional cloud computing services because of its usability, flexibility to move between providers, performance benefits, and cost advantage.
Cloud providers use Akash mainly because it allows them to earn profits from either dedicated or temporarily unused capacity. A computing unit (CPU) is leased as a container unit of software that packages up code and all its dependencies to ensure the application runs quickly and reliably from one environment to the other.
Interestingly, anyone with a computer or server can slice its resources into container units using a virtualization process. All marketplace transactions take place on the Akash Blockchain. To lease a container, the developer requests a deployment by specifying the type of units and the amount they need. An order is then created in the order book (after approval by a validator). The provider that matches all requirements then places a bid, and the provider that bids the lowest amount on the order wins. For every successful lease, a portion of the lease amount is paid to the blockchain.
The Akash Blockchain and Token
The vision of the Akash cloud is a permissionless, sovereign, and open cloud on which builders of the Internet have more considerable freedom to create. Through the containing technology mentioned in the previous paragraph and a unique staking model that we will discuss a bit further down in this article, Akash has become a faster, efficient, and low-cost cloud built for DeFi, decentralized projects, and even high growth companies.
Akash competes at a 10x lower rate than the market standard. The serverless computing platform is compatible with all cloud providers and applications that run on the cloud, making it easy to have Akash integrated with a company’s existing technology stack.
According to the network itself, as the world’s first decentralized cloud computing marketplace, Akash leverages 85% of underutilized cloud capacity in 8.4 million data centers. Akash enables anyone to buy and sell cloud computing.
So, the Akash Network blockchain provides a layer of trust in an otherwise decentralized and trustless environment. The blockchain earns its trust through an open and transparent platform. Data on the chain is an immutable and public record of all transactions, including each provider’s fulfillment history. Moreover, Akash is also politically decentralized; no single entity controls the network, and no intermediary facilitates transactions. That means there is no one incentivized to control or extract revenue from the network.
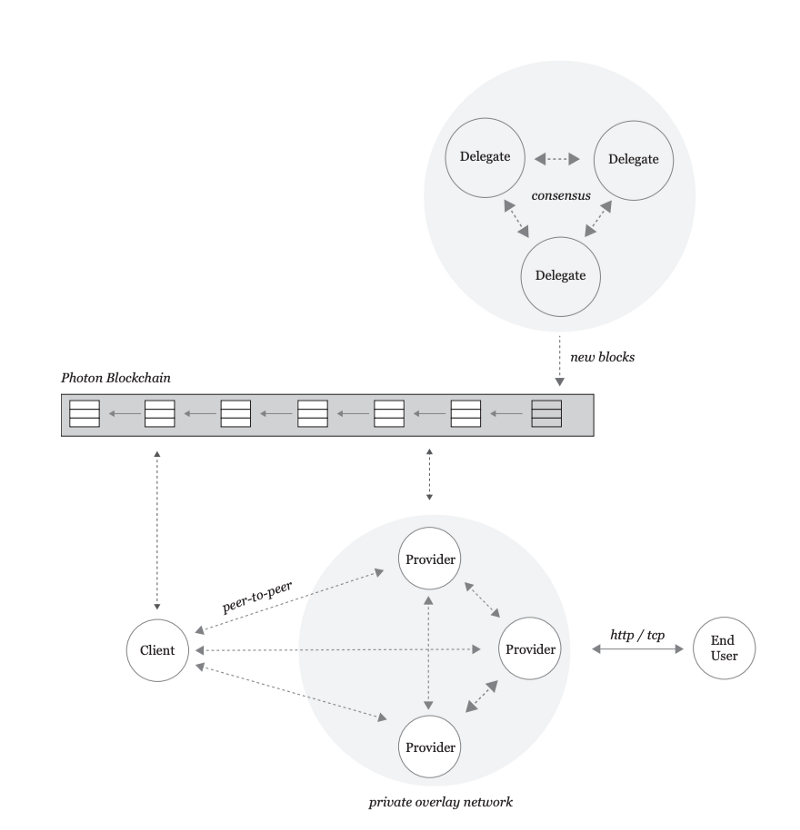
In the image below, first published by Akash Network, you can see how communications and transactions between providers and lenders work on the network.
Core to the Akash network is a token economic model that uses a native asset called Akash token (AKT) to solve the volatility issues and ensures the financial security of the platform’s public blockchain. The AKT has three main functions: to resolve, reward, and reserve. Furthermore, the blockchain relies on a set of validators to vote on proposals. Each proposal is weighed by the voting power, which is the total tokens they staked and the tokens bonded to them.
- For the Market cap and other current information about the Akash Token, click here.
Final Thoughts
At Stakin, we’ve been supporting Akash since the first Akashian Challenge Testnet, both as a validator but also as DeCloud testers and builders. Deploying on Akash is a super smooth experience. Compared to other blockchain cloud products, Akash is much more advanced as what you can deploy on Akash goes far beyond simple storage.
Possibilities are limitless and the serverless approach of Akash even makes deployments more efficient. For a few ideas (including guides) of what you can deploy, have a look through Awesome Akash. It includes Dapps such as PancakeSwap, WordPress, and even blockchain nodes (Akash nodes can run on Akash DeCloud, isn’t that super cool?😎).
We believe that Akash could be a cornerstone to a more decentralized web in the future, as Akash builders will be using a very global and diverse set of servers, as opposed to the traditional players from the cloud oligopoly. Read our article on Why DeCloud is Important for DeFi for further thoughts on that.
If you want to support our activities on Akash, you can delegate to our node! We’re running under Stakin:
akashvaloper12fnzqmnja37mf2y9m6r3dleq5n3jkz7pfkpzmy
DISCLAIMER: This is not financial advice. Staking, delegation, and cryptocurrencies involve a high degree of risk, and there is always the possibility of loss, including the failure of all staked digital assets. Additionally, delegators are at risk of slashing in case of security or liveness faults on some protocols. We advise you to do your due diligence before choosing a validator.